Dan Goodin
Far more than 4,000 Google Play applications silently accumulate a record of all other installed applications in a facts grab that lets developers and advertisers to make thorough profiles of people, a recently published analysis paper discovered.
The apps use an Android-presented programming interface that scans a cellphone for facts about all other applications set up on the cell phone. The application details—which contain names, dates they had been 1st mounted and most just lately updated, and more than three-dozen other categories—are uploaded to remote servers with out permission and no notification.
IAM what IAM
Android’s set up application methods, or IAMs, are software programming interfaces that make it possible for apps to silently interact with other packages on a device. They use two methods to retrieve many varieties of details relevant to mounted apps, neither of which is categorized by Google as a sensitive API. The deficiency of this kind of a designation will allow the strategies to be utilized in a way that is invisible to consumers.
Not all apps that obtain specifics on other set up apps do so for nefarious needs. Developers surveyed by the scientists behind the new paper stated the collection is the basis for launcher apps, which let for the customization of the homescreen and offer shortcuts to open up other apps. IAMs are also applied by VPNs, backup software package, notification supervisors, anti-malware, battery savers, and firewalls.
But the details get can also be employed by advertisers and builders to assemble a in depth profile of customers, the researchers noted in their paper, titled Go away my Applications By yourself! A Review on how Android Builders Accessibility Put in Apps on User’s Unit. They cited previous scientific studies these types of as this a single, which located that a solitary snapshot of applications mounted on a unit authorized scientists to predict the user’s gender with an accuracy of all over 70 per cent. Follow-on results by the identical scientists expanded the demographics that could be deduced to features these types of as religion, partnership status, spoken languages, and international locations of interest. A review by unique scientists stated person demographics also provided age, race, and profits. The investigate also located that a user’s gender could be predicted with an 82 per cent precision price.
“As other privateness-delicate elements of the Android system are guarded by app permissions, forcing developers to explicitly notify customers before making an attempt obtain to these areas, [it] begs the issue on why IAMs are taken care of in another way,” the scientists, from the College of L’Aquila in Italy, Vrije University in Amsterdam, and ETH in Zurich, wrote in the newest paper. “Indeed, the European Union General Info Defense Regulation (GDPR), frequently regarded as the forefront in privateness rules, considers ‘online identifiers supplied by their products, applications, resources, and protocols’ […] as own details, for all uses and implies.”
Adjustments
The new report claimed that Google is thinking about numerous adjustments to Android that have currently been added to a beta version of edition 11 (standard launch has been scheduled for the third quarter, but it’s not obvious if that timeframe will be pushed back again as a final result of disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic). Less than the regarded transform, for an application to interact with other applications, the developer must both (1) explicitly declare in the app manifest—a file that describes vital information about the app—the apps they want to examine or (2) require a new permission called Question_ALL_Deals, whose exact purpose remains unclear to some developers.
The adjust, the scientists stated, even now doesn’t address a person of the main shortcomings of the IAMs abuse, which is the deficiency of discover to people that an application calls for a perhaps privateness-invading permission. Under the regarded as improve, applications nevertheless would not be expected to disclose their selection of details about all other installed apps. Google reps didn’t answer to an email inquiring about planned alterations in Android and requesting a extra basic remark for this write-up.
Application spying
The scientists studied 14,342 free Android apps in the Google Perform Retail outlet and 7,886 open up resource Android apps and analyzed the apps’ use of IAMs. The researchers uncovered that 4,214 of the Google Enjoy apps, representing a little a lot more than 30 p.c of those people studied, utilized IAMs. Only 228 of the open up supply apps, or a little significantly less than 3 %, gathered information of other applications. With more than 3 million apps offered in the Google-hosted services, the genuine range of prying applications is practically surely an get of magnitude bigger than the 4,214 discovered in the review.
In descending order, the best five Google Participate in app types that most regularly collected the information have been: Online games (73 per cent), Comics (71 %), Personalization (61 %), Autos and Autos (54 per cent), and Relatives (43 per cent). The figure down below lists the use of IAMS across all classes.
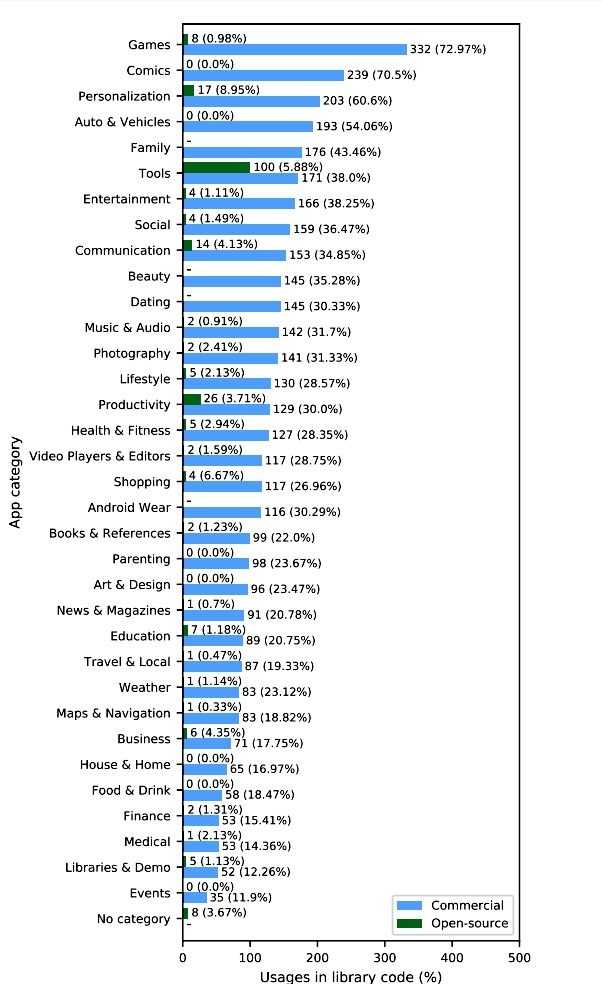
Soccia et al.
The paper didn’t discover any of the apps by identify.
The extensive majority of the Google Participate in apps that gathered app data—84 percent—did so employing third-bash code libraries. The scientists discovered 56 ad libraries that gathered the facts and uncovered that a “small number” of them accounted for far more than a third of all IAMs usages by bundled libraries. Other bundles discovered were utility libraries, tailor made libraries, and analytics and app-advertising libraries. Below is a table listing the major 20 most common libraries:
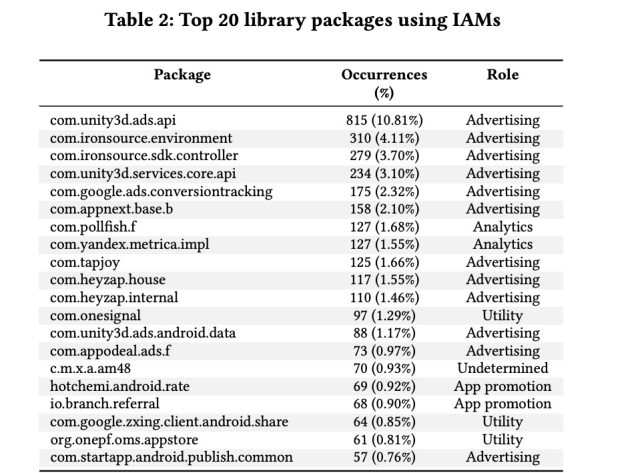
Soccia et al.
“In the discussion of benefits, we assumed that [the] large bulk of the IAMs phone calls performed by advertisement libraries are for profiling uses, and we therefore recommended some opportunity adjustments to the Android system accordingly,” the researchers wrote. Chief between the suggestions was that consumers receive notification that an app is requesting authorization to accessibility other installed apps. Like other permissions requests, it should give users the skill to refuse.
The researchers claimed Apple’s iOS makes use of approaches equivalent to IAMs to let apps to monitor other installed apps. The researchers went on to say that in new versions of the OS, “applications of desire have to be preemptively declared within the application… manifest file, and consequently are reviewed by app keep moderators ahead of publication.”
As famous earlier, there are legit good reasons for applications to obtain aspects of other mounted applications. But there is also reason for concern. This most current study only reinforces the guidance I have long specified that Android apps really should be put in sparingly and only when they deliver a obvious reward. It also will help to favor cost-based apps above no cost types, considering the fact that the latter group is additional probably to count on ads for income. Open up resource apps are also revealed to gather less app data, but they also call for customers to enable installations from third-occasion marketplaces.




